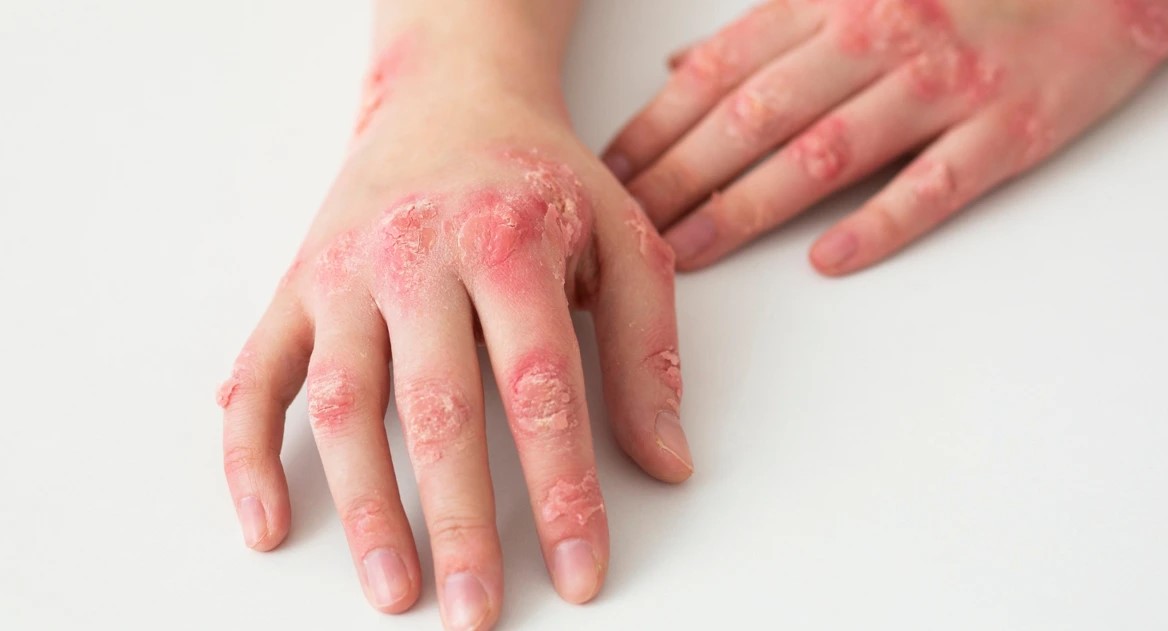
Hey there! Are you familiar with the term dermatitis? It may sound like a complex medical condition, but it’s actually just a fancy word for skin inflammation. Dermatitis can cause redness, itchiness, and even blistering. It can be a real pain, but don’t worry, I’m here to help you understand more about it!
There are various types of dermatitis, each with its own unique characteristics. In this article, we’ll explore the most common types: atopic dermatitis (AD), contact dermatitis (CD), seborrheic dermatitis (SD), dyshidrotic eczema (DE), nummular eczema (NE), stasis dermatitis (SD), and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD). So, let’s dive in and learn more about each of them!
Atopic Dermatitis (AD)
First up, we have atopic dermatitis. This is the most common and well-known form of dermatitis, often referred to as eczema. It usually begins in infancy or childhood, and in some cases, it can persist into adulthood.
People with AD often have dry and sensitive skin, which can be easily irritated. This can lead to intense itching and a rash that typically appears on the face, neck, and hands. Environmental factors, such as allergens and irritants, can trigger flare-ups.
To manage AD, it’s important to keep the skin moisturized and avoid potential triggers. Using gentle skincare products and wearing soft, breathable fabrics can also help prevent irritation. In severe cases, a doctor may prescribe topical corticosteroids or other medications to reduce inflammation.
Contact Dermatitis (CD)
Next on our list is contact dermatitis. As the name suggests, this type of dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with an irritating substance or allergen. Common culprits include certain metals (like nickel), cosmetics, cleaning products, and even certain plants.
CD can cause redness, itching, and sometimes even blisters in the affected area. The key to managing CD is identifying and avoiding the trigger. If you suspect a particular substance is causing your symptoms, try to eliminate it from your environment and see if your skin improves. If the symptoms persist or worsen, it’s best to consult a dermatologist for further evaluation and treatment options.
Seborrheic Dermatitis (SD)
Now, let’s talk about seborrheic dermatitis. This form of dermatitis is often associated with oily and sensitive skin. It commonly affects the scalp, causing dandruff, but can also occur on the face, chest, and other areas with a high concentration of oil glands.
SD can cause redness, flaking, and itching in the affected areas. While the exact cause is unknown, factors such as hormonal imbalances, stress, and certain yeast overgrowth may contribute to its development.
To manage seborrheic dermatitis, regular cleansing with mild shampoos or soaps can help control the symptoms. In some cases, medicated shampoos or topical creams prescribed by a dermatologist may be necessary to effectively treat the condition.
Dyshidrotic Eczema (DE)
Another type of dermatitis is dyshidrotic eczema. This condition is characterized by small, itchy blisters that typically develop on the hands and feet. The exact cause of DE is unknown, but factors such as stress, allergies, and exposure to certain metals or solvents may trigger flare-ups.
Managing dyshidrotic eczema involves keeping the affected areas moisturized and protected. Avoiding potential triggers, such as contact with irritants or allergens, is also crucial. In severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe topical medications or recommend light therapy to alleviate symptoms.
Nummular Eczema (NE)
Nummular eczema, also known as discoid eczema, is characterized by round or oval-shaped patches of inflamed skin. These patches can be itchy, dry, and occasionally blistered. NE often occurs on the arms and legs, but can appear anywhere on the body.
Moisturizing the skin regularly is essential in managing nummular eczema. Avoiding harsh soaps and detergents, as well as using mild, fragrance-free products, can also help prevent flare-ups. In some cases, a doctor may prescribe topical corticosteroids or other medications to reduce inflammation and itching.
Stasis Dermatitis (SD)
Next up, we have stasis dermatitis. This type of dermatitis is commonly seen in individuals with poor circulation, often due to conditions like varicose veins or congestive heart failure. It primarily affects the lower legs and ankles.
Stasis dermatitis can cause redness, swelling, and itching in the affected areas. Elevating the legs, wearing compression stockings, and regularly moisturizing the skin can help manage symptoms. In severe cases, a doctor may recommend specific treatments to improve circulation and prevent complications.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis (ACD)
Last but not least, we have allergic contact dermatitis. This form of dermatitis occurs when the immune system reacts to a specific allergen that comes into contact with the skin. Common allergens include certain metals, fragrances, preservatives, and latex.
ACD can cause redness, swelling, and itching in the affected area. Identifying and avoiding the trigger is crucial in managing this type of dermatitis. If symptoms persist, a dermatologist may conduct patch testing to determine the specific allergen causing the reaction and recommend appropriate treatment options.
And there you have it! A brief overview of the most common types of dermatitis. Remember, if you suspect you have any form of dermatitis, it’s always a good idea to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Identifying the Symptoms
How do you know if you have contact dermatitis? Well, the symptoms can vary depending on the individual and the substance involved. But generally, you can look out for these telltale signs:
- Redness and inflammation: The affected area may turn red, swollen, and feel warm to the touch. It can be quite alarming, but try not to scratch or rub the area too much, as it may worsen the symptoms.
- Itching and discomfort: One of the most frustrating parts of contact dermatitis is the intense itching. It can be so tempting to scratch, but doing so can lead to further irritation and potential infection.
- Blisters or oozing: In some cases, contact dermatitis may cause small blisters or even oozing sores. This is more common with certain substances, like chemicals or plants.
- Dryness and scaling: As the rash starts to heal, you may notice your skin becoming dry and flaky. This is normal and should resolve over time.
Managing Contact Dermatitis
If you suspect that you have contact dermatitis, there are a few steps you can take to manage the symptoms and help your skin heal:
- Avoid the irritant: The first and most important step is to identify and avoid the substance that caused the reaction. If you can pinpoint the culprit, do your best to steer clear of it in the future.
- Keep your skin moisturized: Applying a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer can help soothe the affected area and prevent further dryness. Look for products specifically designed for sensitive skin.
- Use over-the-counter creams: There are various over-the-counter creams and ointments available that can provide relief from itching and inflammation. Look for ones that contain hydrocortisone or calamine lotion.
- Cool compresses: Placing a cool, damp cloth or ice pack on the affected area can help alleviate itching and reduce inflammation.
- Seek medical advice: If your symptoms are severe, persist for more than a few weeks, or if you develop an infection, it’s important to seek medical advice. Your doctor may prescribe stronger medications or recommend further treatment options.
Remember, contact dermatitis can be a pesky condition, but with the right care and precautions, you can manage the symptoms and prevent future flare-ups. If you’re unsure about the cause of your rash or if it doesn’t improve with self-care, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance.
Contact Dermatitis (CD)
Have you ever had a red, itchy rash that appeared out of nowhere? Chances are, you may have experienced contact dermatitis. It’s a common skin condition that occurs when your skin comes into contact with an irritating substance. Let’s dive into the world of contact dermatitis and learn more about this bothersome condition.
So, what exactly is contact dermatitis? Well, it’s an inflammation of the skin that occurs when your skin reacts to a substance it has come into contact with. This could be anything from certain metals, cosmetics, fragrances, cleaning products, or even plants like poison ivy. The reaction typically happens within a few hours or a few days after exposure, and it can be quite uncomfortable.
Identifying the Symptoms
How do you know if you have contact dermatitis? Well, the symptoms can vary depending on the individual and the substance involved. But generally, you can look out for these telltale signs:
- Redness and inflammation: The affected area may turn red, swollen, and feel warm to the touch. It can be quite alarming, but try not to scratch or rub the area too much, as it may worsen the symptoms.
- Itching and discomfort: One of the most frustrating parts of contact dermatitis is the intense itching. It can be so tempting to scratch, but doing so can lead to further irritation and potential infection.
- Blisters or oozing: In some cases, contact dermatitis may cause small blisters or even oozing sores. This is more common with certain substances, like chemicals or plants.
- Dryness and scaling: As the rash starts to heal, you may notice your skin becoming dry and flaky. This is normal and should resolve over time.
Managing Contact Dermatitis
If you suspect that you have contact dermatitis, there are a few steps you can take to manage the symptoms and help your skin heal:
- Avoid the irritant: The first and most important step is to identify and avoid the substance that caused the reaction. If you can pinpoint the culprit, do your best to steer clear of it in the future.
- Keep your skin moisturized: Applying a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer can help soothe the affected area and prevent further dryness. Look for products specifically designed for sensitive skin.
- Use over-the-counter creams: There are various over-the-counter creams and ointments available that can provide relief from itching and inflammation. Look for ones that contain hydrocortisone or calamine lotion.
- Cool compresses: Placing a cool, damp cloth or ice pack on the affected area can help alleviate itching and reduce inflammation.
- Seek medical advice: If your symptoms are severe, persist for more than a few weeks, or if you develop an infection, it’s important to seek medical advice. Your doctor may prescribe stronger medications or recommend further treatment options.
Remember, contact dermatitis can be a pesky condition, but with the right care and precautions, you can manage the symptoms and prevent future flare-ups. If you’re unsure about the cause of your rash or if it doesn’t improve with self-care, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance.